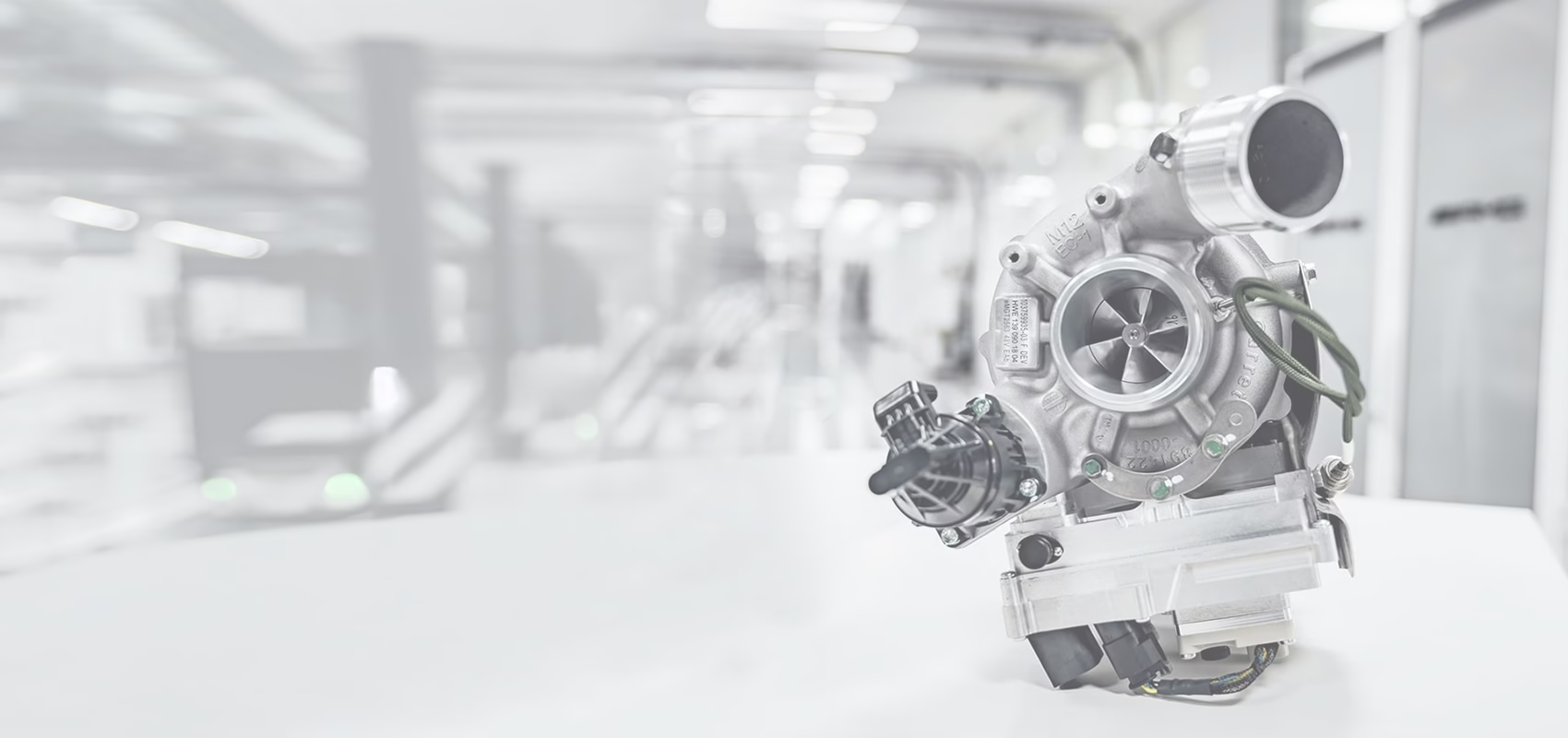
Turbocharger stands as one of the core technologies in modern automotive engineering for achieving high-efficiency power output. Functioning as an exhaust energy recovery system for internal combustion engines, it constitutes a coaxial assembly comprising a turbine and a centrifugal compressor. Precision-coupled via a floating bearing system, the turbine housing and compressor form a high-speed rotor assembly capable of exceeding 150,000 revolutions per minute (RPM).
Principle of Efficiency Innovation:
High-temperature exhaust gases (600-900°C) expelled from the engine drive the radial-flow turbine within the turbine housing. This rotational energy is transmitted through the coaxial shaft to the compressor impeller, which pressurizes ambient air to 1.3-2.5 bar. Following intercooler-mediated temperature reduction, the oxygen-enriched high-density charge air enhances fuel combustion efficiency by over 30%. This thermodynamic principle enables a 1.5-liter turbocharged (1.5T) engine to deliver power output equivalent to that of a 2.0-liter naturally aspirated (2.0L) engine.
Key technical specifications:
Turbine blade tip speed: ≥450 m/s
Compressor adiabatic efficiency: 72-78%
Intercooler effectiveness: 85-93%
Boost pressure linearity: Achieved within 90% of engine RPM range
This energy recovery mechanism transforms waste heat from exhaust flow into usable mechanical work, exemplifying sustainable engineering practices in modern powertrain design.